From the charter of the Working Group:
The XML Linking WG continues the effort begun in the XML WG in January 1997.
The objective of the XML Linking WG is to design advanced, scalable, and maintainable hyperlinking and addressing functionality for XML. Such functionality includes the hyperlinking abilities of HTML, but extends them to include at least the following:
XLink defines the following:
http://wwww.w3.org/namespace/xlink/1999/
An XLink processor expected to detects those contructs so they are handled at the application level.
However XLink does not enforce behaviour, this is application dependant with hints defined on the link elements.
The core properties (attributes):
xlink:type attribute indicates the type of the link:
simple simple link
extended extended link
xlink:href this is the only locator attribute, and
its value is an URI-Reference [RFC 2396].
xlink:locator are elements contained in extended links
and defining resources paritcipating in the link. Each locator
holds an xlink:role attribute allwoing to reference it.
xlink:arc are elements contained in extended links
and defining traversal behaviour using the following attributes:
xlink:from the source of the arc, the attribute value
target a locator referenced by its xlink:role name
xlink:to the destination of the arc
Those are attribute holding behaviour related informations:
xlink:show indicate expected behaviour on traversal effect:
embed the link target should be included like <IMG>
new the link target should create a new rendering,
like opening a new window.
replace the link target should replace the resource
containing the link, like <A> in most cases.
xlink:actuate indicate expected triggering of link:
auto indicate at link detection time, like <IMG>
if autoloading of images is turned on.
onRequest indicate activation at user's request,
like <A>
Those are placeholders for application semantic:
xlink:title is designed to provide human-readable
text describing the links, simple links must use an attribute while extended
links must use an element.
xlink:role is an attribute containing a
qualified name
used to describe the function of the link's or locator's content.
for example XLink uses role="xlink:external-linkset"
to distinguish Links Sets from Extended links.
Here are the limitations on simple links:
But they benefit from a lighter syntax
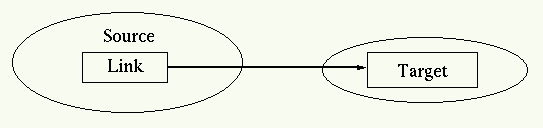
this can be as simple as:
<students xlink:href="students.xml"> The list of students.</students>
assuming the following element declaration:
<!ELEMENT student ANY> <!ATTLIST student xmlns:xlink CDATA #FIXED "http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink/namespace/" xlink:type CDATA #FIXED "simple" xlink:href CDATA #REQUIRED xlink:role CDATA #IMPLIED xlink:title CDATA #IMPLIED xlink:show (new|embed|replace) "replace" xlink:actuate (onRequest|auto) "onRequest" >
Here is a set of "advanced" features:
xlink:locator elements
xlink:arc elements
xlink:title elements (I18N)
<element xmlns:xlink="http://www.w3.org/1999/namespace/xlink/"
xlink:type="extended">
<xlink:locator href="Source" role="role1"/>
<xlink:locator href="Target" role="role2"/>
<xlink:arc from="role1" to="role2"
show="embed" actuate="auto"/>
<xlink:title>The link title<xlink:title/>
<xlink:title xml:lang="fr">Description du lien<xlink:title/>
...
</element>
This construct allows to reference an external set of links
xlink:extended but with
xlink:role="xlink:external-linkset"
<xlink:extended xmlns:xlink="http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink/namespace/"
role="xlink:external-linkset">
<xlink:title>DV's Links</xlink:title>
<xlink:locator href="mylinkset.xml"/>
</xlink:extended>
There is still some issues left like:
But the core is now stable.
May the mission complete sucessfully...
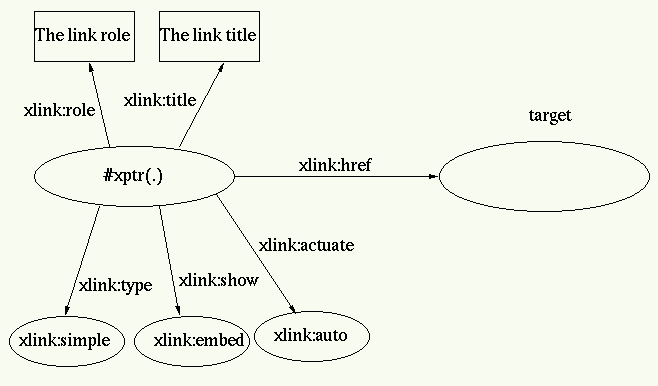
<element xmlns:xlink="http://www.w3.org/namespace/xlink/1999/"
xlink:href="target"
xlink:type="simple"
xlink:show="embed"
xlink:actuate="auto"
xlink:role="The link role"
xlink:title="The link title">
...
</element>
translates to
<element>
<rdf:RDF xmlns:rdf="http://www.w3.org/1999/02/22-rdf-syntax-ns#"
xmlns:xlink="http://www.w3.org/namespace/xlink/1999/">
<rdf:Description about="#xptr(../..)">
<xlink:href rdf:resource="target"/>
<xlink:type rdf:resource="xlink:simple"/>
<xlink:show rdf:resource="xlink:embed"/>
<xlink:actuate rdf:resource="xlink:auto"/>
<xlink:role>The link role</xlink:role>
<xlink:title>The link title</xlink:title>
</rdf:Description>
</rdf:RDF>
...
</element>
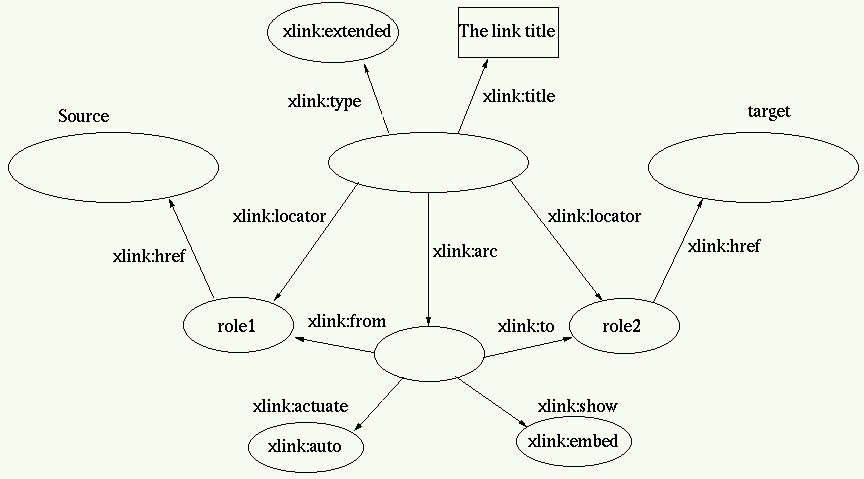
<element xmlns:xlink="http://www.w3.org/1999/namespace/xlink/"
xlink:type="extended">gt;
<xlink:locator href="Source" role="role1"/>gt;
<xlink:locator href="Target" role="role2"/>gt;
<xlink:arc from="role1" to="role2"
show="embed" actuate="auto"/>gt;
<xlink:title="The link title"/>gt;
...
</element>gt;
translates to
<element>gt;
<rdf:rdf xmlns:rdf="http://www.w3.org/1999/02/22-rdf-syntax-ns#"
xmlns:xlink="http://www.w3.org/1999/namespace/xlink/">gt;
<rdf:description about="#xptr(../..)">gt;
<xlink:type rdf:resource="xlink:extended"/>gt;
<xlink:locator rdf:about="source" rdf:id="role1"/>gt;
<xlink:locator rdf:about="target" rdf:id="role2"/>gt;
<xlink:arc>gt;
<xlink:from rdf:resource="#role1">gt;
<xlink:to rdf:resource="#role2">gt;
<xlink:show rdf:resource="xlink:embed"/>gt;
<xlink:actuate rdf:resource="xlink:auto"/>gt;
</xlink:arc>gt;
<xlink:title>gt;the link title</xlink:title>gt;
</rdf:description>gt;
</rdf:rdf>gt;
...
</element>gt;